Understanding the Role of a Centerless Grinder Operator
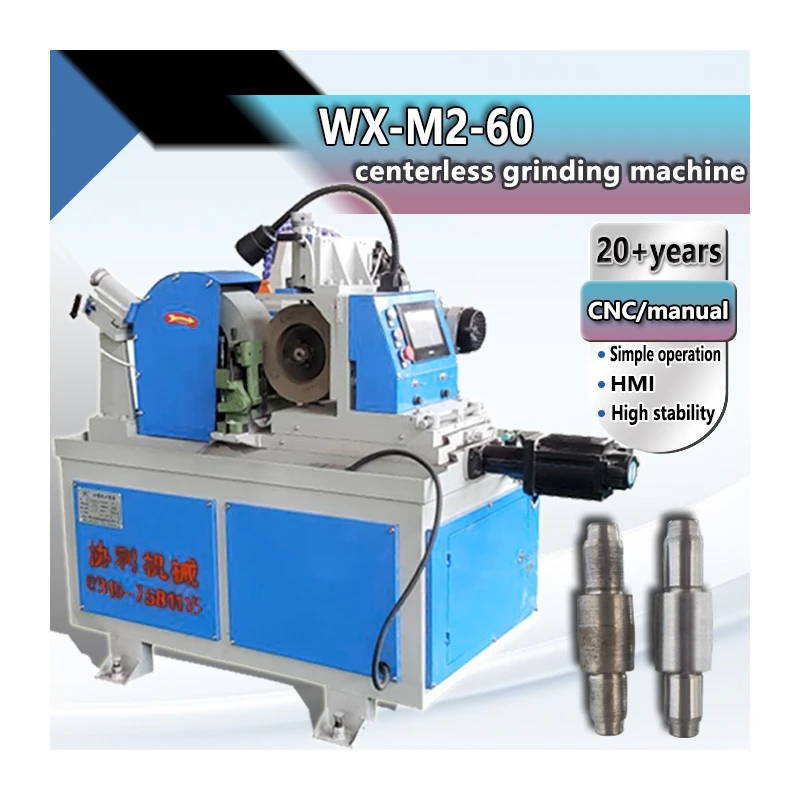
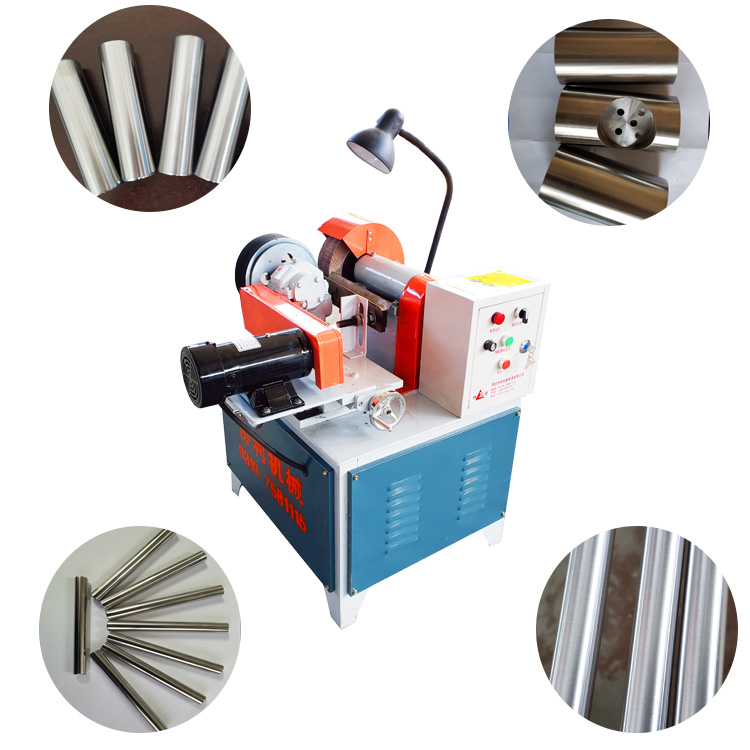
In the manufacturing sector, precision and efficiency are paramount. One key player in achieving these goals is the centerless grinder operator. A centerless grinder is a type of industrial machine used to grind workpieces that do not require fixtures for holding, resulting in significant advantages in speed and uniformity during the grinding process. Understanding the responsibilities, requirements, and importance of a centerless grinder operator can provide insight into the role they play in modern manufacturing.
The Role of a Centerless Grinder Operator
The primary responsibility of a centerless grinder operator is to manage and operate the centerless grinding machine. This involves setting up the machine, selecting the appropriate grinding wheels, calibrating the equipment, and monitoring the process to ensure that the final products meet specified tolerances and dimensions. The operator also needs to perform regular maintenance checks on the machine, troubleshoot issues, and make necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
Skills and Qualifications
To become a successful centerless grinder operator, certain skills and qualifications are essential. A high school diploma or equivalent is typically required, but additional technical training or vocational courses in machining or manufacturing can be advantageous. Operators must possess a strong understanding of machining principles, geometry, and material properties, as they often work with various metals and other materials.
Attention to detail is critical in this role, as even minor deviations in the machine setup can lead to significant errors in product dimensions. Problem-solving skills are also essential, as operators must quickly identify and address issues that arise during production. Finally, familiarity with safety protocols and machine operation standards is crucial, ensuring a safe working environment for everyone on the shop floor.
Importance in Manufacturing
buy centerless grinder operator

The role of a centerless grinder operator is vital in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Precision ground components are necessary for the functioning of many mechanical systems, from engines to intricate machinery. The ability to produce high-quality parts consistently can significantly impact a company’s overall efficiency and profitability.
Centerless grinding offers several advantages over traditional grinding methods. It allows for higher production rates and improved accuracy since multiple workpieces can be ground simultaneously without the need for complex fixturing. This can lead to reduced manufacturing costs and faster turnaround times, making centerless grinding a preferred choice in many applications.
Challenges Faced
While the role can be rewarding, it comes with its challenges. The operator must be able to work under pressure, especially in high-demand environments where production speed is crucial. Additionally, operators are often required to manage multiple tasks simultaneously, from machine operation to quality control and maintenance. The constant need for precision can be mentally and physically demanding, which underscores the importance of training and experience in this field.
The Future of Centerless Grinding
As technology continues to evolve, centerless grinding machines are becoming increasingly sophisticated, incorporating automation and advanced computer controls. Operators will need to adapt to these changes, necessitating ongoing education and training to keep up with the latest advancements in the industry.
In conclusion, centerless grinder operators play a crucial role in the manufacturing landscape. By understanding their responsibilities, skills, and the importance of their work, one can appreciate the significant contribution they make to producing high-quality, precision-engineered parts. As the industry evolves, so too will the role of the centerless grinder operator, ensuring their continued relevance and importance in the manufacturing process.