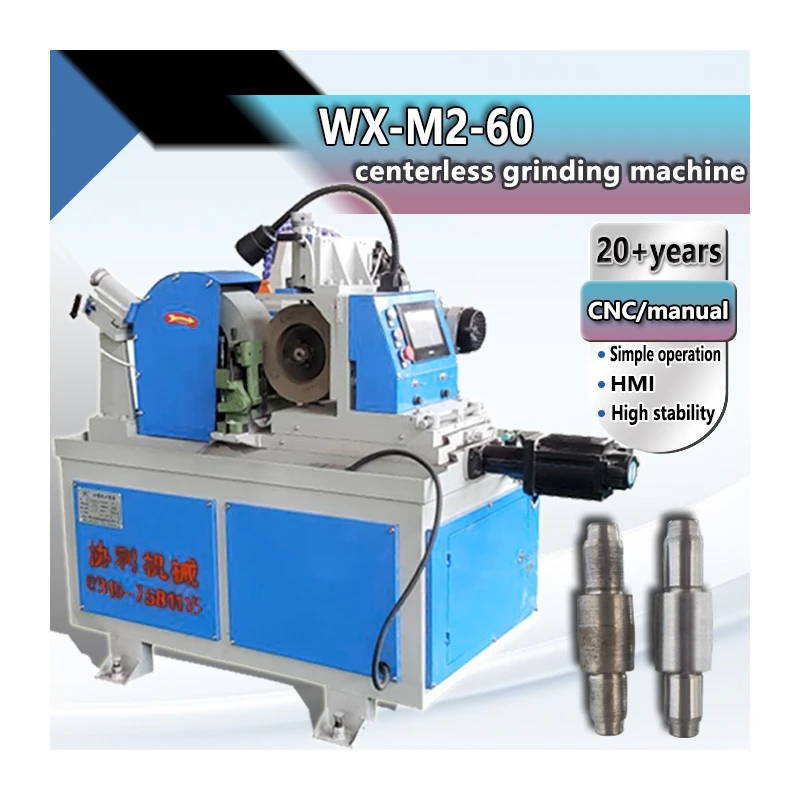
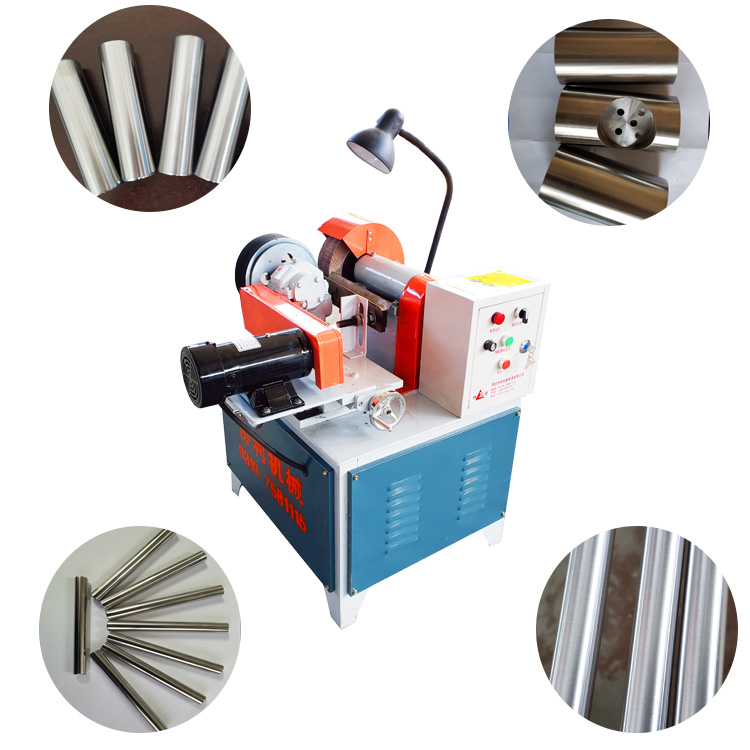
Understanding OSHA Standards for Centerless Grinders in OEM Facilities
Centerless grinders are vital machines in the manufacturing industry, predominantly used for precision grinding of various materials. They play a critical role in producing components for different applications, from automotive parts to medical devices. However, with the efficiency and productivity they bring, there is also a need for stringent safety measures, particularly in Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) settings. This is where the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards come into play.
The Importance of OSHA in Manufacturing
OSHA, a division of the United States Department of Labor, was established to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for employees. The agency sets and enforces standards that employers must follow to minimize risks associated with workplace hazards. In the context of OEM facilities utilizing centerless grinders, adherence to OSHA regulations is critical for ensuring employee safety.
Hazards Associated with Centerless Grinders
Centerless grinders can pose numerous hazards if not managed correctly. Common risks include
1. Mechanical Hazards The moving parts of a grinder can cause severe injuries, from lacerations to amputations. Employees can be caught in rotating machinery or come into contact with the grinding wheel.
2. Noise Exposure Grinding operations can generate high noise levels that may lead to hearing loss over time if proper measures are not taken.
3. Chemical Hazards The use of cutting fluids in grinding processes can expose workers to harmful chemicals, potentially leading to skin and respiratory problems.
4. Ergonomic Risks Improper workstation setup can lead to musculoskeletal disorders among operators who perform repetitive tasks over extended periods.
OSHA Standards Applicable to Centerless Grinders
To mitigate these risks, OSHA has laid out several standards relevant to the operation of centerless grinders in OEM environments
. Some key standards includeoem osha centerless grinder

1. Machine Guarding (29 CFR 1910.212) OSHA mandates that machinery must have appropriate guards in place to protect operators from moving parts. This includes proper guards on grinding wheels to prevent fragments from flying off during operation.
2. Hearing Conservation (29 CFR 1910.95) If noise levels exceed the permissible limits, employers are required to implement a hearing conservation program. This ensures that workers are regularly tested for hearing impairment and provided with hearing protection when necessary.
3. Hazard Communication (29 CFR 1910.1200) Employers must inform employees about the chemicals they are exposed to, including those in cutting fluids. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) should be readily available, and proper training on handling, storage, and emergency measures should be provided.
4. Ergonomics While OSHA does not have a specific ergonomic standard, it encourages employers to address ergonomic hazards in the workplace. This includes evaluating the layout of grinding stations, ensuring they promote good posture and reduce repetitive strain.
Implementing Safety Practices in OEM Facilities
To enhance safety in OEM facilities with centerless grinders, employers should adopt proactive measures such as
- Regular Training Conduct safety training sessions to educate employees on the proper use of machinery, as well as the risks involved. Familiarity with safety protocols increases overall workplace safety.
- Routine Inspections Regular inspections of grinding equipment ensure that all safety devices are functioning correctly. Any worn or damaged parts should be replaced immediately.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Employers should provide appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and ear protection, to minimize the impact of potential hazards.
- Environmental Controls Implementing proper ventilation systems can help manage exposure to harmful fumes and particulate matter generated during the grinding process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while centerless grinders are essential for manufacturing operations, they come with inherent risks that must be managed effectively. By understanding and complying with OSHA standards, OEM facilities can create a safer working environment for their employees. The emphasis on safety not only protects workers but also enhances productivity and morale, ultimately benefiting the business as a whole. Adopting a comprehensive safety culture should be a priority for all OEMs that operate centerless grinders.